[コンプリート!] yield stress units 285447-What is yield stress
Strength is a critical factor in metal uses, for example, some applications require stronger aluminum parts, while some products need high steel hardness or yield strength of steel, this may determine the selection of CNC machining material or product design Here we collect the metal strength chart (tensile, yield strength, hardness, and density included) and mechanical properties chart ofThe shear yield stress k of a polycrystalline solid is related to the shear stress τy required to move a dislocation on a single slip plane k τy 2 ≈ 3 The uniaxial yield stress σy of a polycrystalline solid is approximately σy =2k, where k is the shear yield stress Hardness H (in MPa) is given approximately by H ≈3σy6) By comparing the design strength p w with the resultant stress τ r the value of the weld throat thickness is calculated and then the weld size ie if the τ r /p w = 5 then the throat thickess t = 5 units and the weld leg size h = 1,414t
Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau
What is yield stress
What is yield stress-Stress is defined as the force per unit area of plastic and has units Nm 2 or Pa The formula to calculate tensile stress is σ (stress) = F/A Where σ is stress (in Newtons per square metre or, equivalently, Pascals), F is force (in Newtons, commonly abbreviated N), and A is the crosssectional area of the sampleYield strength is the maximum stress that can be applied before it begins to change shape permanently This is an approximation of the elastic limit of the steel If stress is added to the metal but does not reach the yield point, it will return to its original shape after the stress is removed


Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials
This theory states that failure of a piping component occurs when the maximum shear stress exceeds the shear stress at the yield point in a tensile test Brittle vs Ductile Fracture In the tensile test, the fracture point is the point of strain where the material physically separates At this point, the strain reaches its maximum value and theFvw,d design shear resistance of the fillet weld per unit length fw characteristic strength of the weld metal fy yield stress of steel fya average yield strength fyb yield stress of the bolt fyc yield stress of column g length of the gap g1 leg length of fillet weld h, h0, h1 height, height of concrete foundation hc height of column cross sectionBrowse through the page and find the unit you want to convert from Type the value you are converting next to the unit 2 Click the Convert button Your value gets instantly converted to all other units on the page 3 Now find the unit you want and get the conversion result next to it It's your answer
Yield stress refers to the minimum stress at which a material will deform without significant increase in load In other words, the minimum stress required to make a material flow is the yield stress, and it is a measure of the strength of the material structureValue in US Customary Units Value in MKS Units Elastic Modulus of Aluminum Elastic Modulus of Steel Elastic Modulus of PMMA 4 ksi 29 GPa Yield stress of low strength steel 345 MPa Yield stress of very high strength steel A pencil diameter 03 in 76 mm=0076 mWhat is the SI unit of yield strength?
Ultimate tensile strength unit Tensile strength is defined as a measurement of stress, which, in turn, is measured as force per unit area The SI unit of UTS is Pascal or Pa It's usually expressed in megaPascals, so the UTS is commonly expressed in megaPascals (or MPa) In the US, the UTS is often expressed in pounds per square inch (or psi)The load is measured in newton and the area measured in m 2 So the unit of stress is N/ m 2 When the area is expressed in cm or mm, then the stress unit becomes N/cm 2 or N/mm 2 1 N/ m 2 = 10 4 N/cm 2 = 10 6 N/mm 2 1 MN/ m 2 = 10 6 N/ m 2 = 10 2 N/cm 2 = 1 N/mm 2 1 N/ m 2 = 1 PaThe yield stress value of mild steel is 25×108 Pa He wants to check whether his design will withstand the design load Fig3 A design problem, the cantilever should be able to withstand design load The following figure shows the Von Mises stress distribution obtained by FEA analysis of the beam


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
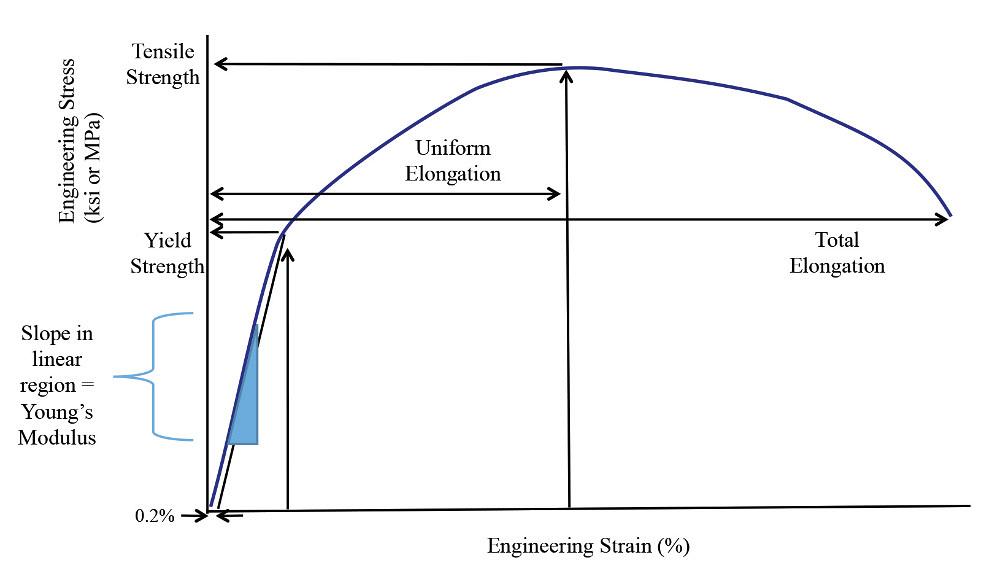
Ultimate stress, whether it is tension, compression, shearing or bending, is the highest amount of stress a material can withstand Yield stress is the stress value at which plastic deformation occurs An accurate value for yield stress can be difficult to pinpointThe most common engineering approximation for yield stress is the 02 percent offset rule To apply this rule, assume that yield strain is 02 percent, and multiply by Young's Modulus for your material \sigma = 0002\times E σ = 0002×EYield stress, marking the transition from elastic to plastic behaviour, length) is proportional to the stress (the load per unit of crosssectional area) This means that, with each increase in load, there is a proportional increase in the rod's length, and, when the load is removed, the rod shrinks to its original size



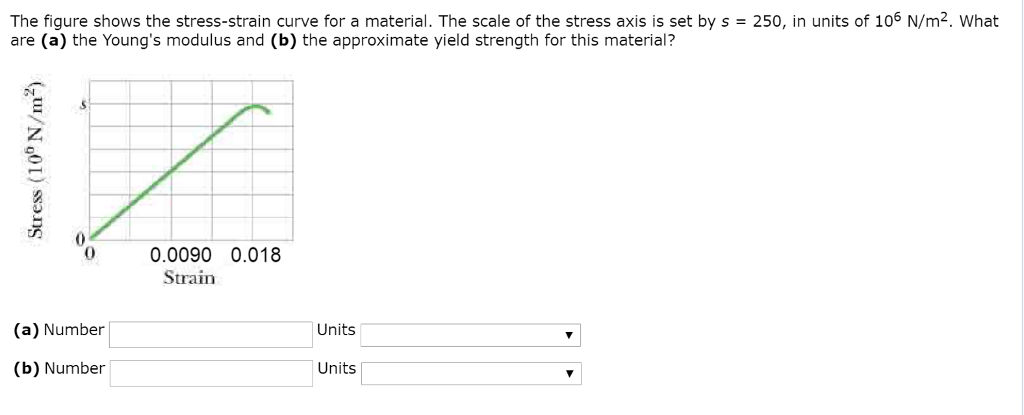
Figure Shows The Strain Stress Curve For A Given Material What Are A Young S Modulus And B Approximate Yield Strength For This Material


Link Springer Com Content Pdf 10 1007 Bf Pdf
2 n Drilling Fluids A parameter of the Bingham plastic modelYP is the yield stress extrapolated to a shear rate of zero (Plastic viscosity, PV, is the other parameter of the Binghamplastic model)A Bingham plastic fluid plots as a straight line on a shear rate (xaxis) versus shear stress (yaxis) plot, in which YP is the zeroshearrate interceptAs yield strength is related to deformation which is a result of applied stress, the SI unit of yield strength is Nm 2 In CGS system, the yield strength is gcm 2 State if the given statement is true or false In drawing deep operations of sheet steels, problems are created by yield point phenomenonRambergOsgood Equation The stressstrain curve is approximated using the RambergOsgood equation, which calculates the total strain (elastic and plastic) as a function of stress where σ is the value of stress, E is the elastic modulus of the material, S ty is the tensile yield strength of the material, and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which can be calculated based on


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs


Getting To Know More About The Metal You Are Forming
F b = 075 F y for D / t ≤ 10, 340 / F y (SI units) is desirable that the ultimate tensile strength for the wheel should lie between the ultimate tensile strength and the yield stress of the pinion Table 32 Allowable stresses on materials for spur, helical, straight bevel, spiral bevel and hypoid bevel gearsCompressive stress stress that tends to compress or shorten the material acts normal to the stressed area;The shear yield stress k of a polycrystalline solid is related to the shear stress τy required to move a dislocation on a single slip plane k τy 2 ≈ 3 The uniaxial yield stress σy of a polycrystalline solid is approximately σy =2k, where k is the shear yield stress Hardness H (in MPa) is given approximately by H ≈3σy



Tensile Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics



Minimum Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
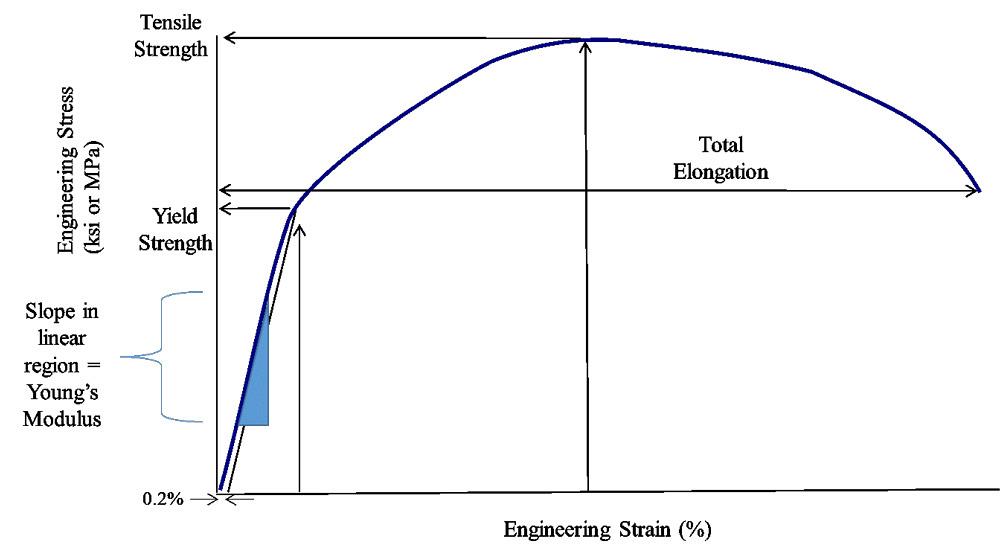
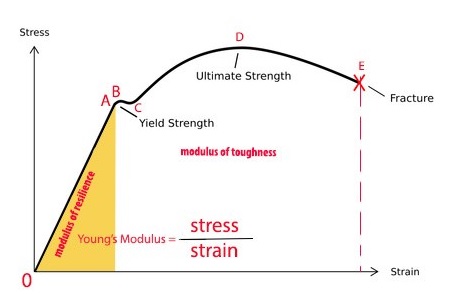
Yield Stress Instruments The YR1 from Brookfield Engineering is an excellent tool for measuring yield stress It is a simpletouse lowcost alternative to complicated, fullfeatured laboratory rheometers The YR1 is designed to be used right on the production floor by techniciansWhere σ el and ε el are the stress and strain at the elastic limit, S ty is the tensile yield strength, and E is the elastic modulus Note that the units of the modulus of resilience are the same as the units of strain energy density, which are psi in US Customary units and Pa in SI unitsYield Strength, Modulus of Elasticity, Ultimate Strength of Selected Materials A straight line is drawn through Point (D) at the same slope as the initial portion of the stressstrain curve The point of intersection of the new line and the stressstrain curve is projected to the stress axis The stress value, in pounds per square inch, is the yield strength It is indicated in Figure 5 as Point 3



Units Of Stress And Strain Nuclear Power Net



Yield Engineering Wikipedia
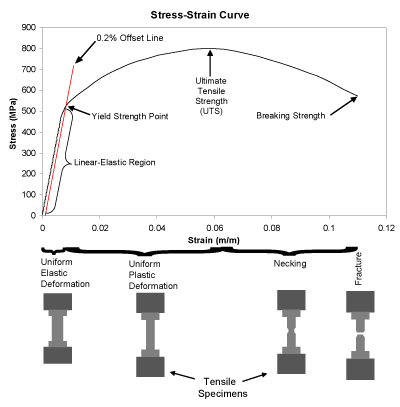
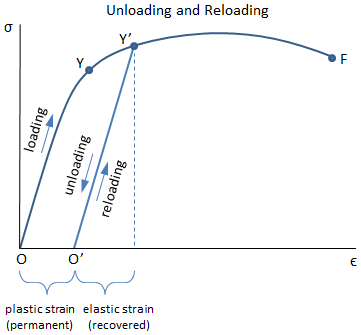
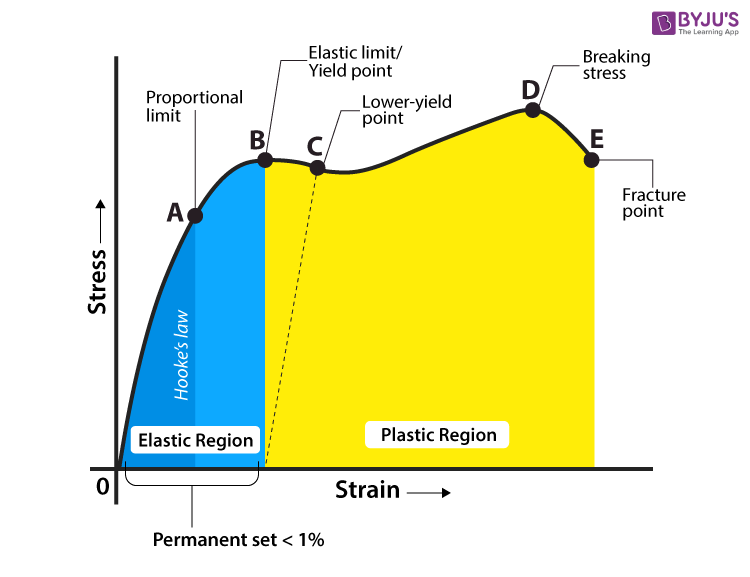
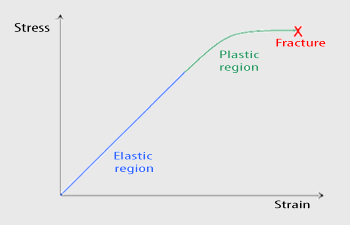
In materials science and engineering, the yield point is the point on a stressstrain curve that indicates the limit of elastic behavior and the beginning of plastic behavior Below the yield point, a material will deform elastically and will return to its original shape when the applied stress is removed Once the yield point is passed, some fraction of the deformation will be permanent and nonreversible and is known as plastic deformation The yield strength or yield stress is a material propThe magnitude of stress at which this transition occurs is known as the material's yield stress or strength The yield strength is a material constant that represents the limit of its elastic behavior Ductile materials like iron boast higher yield strength values than plastics, such as polyethyleneShearing stress stress that tends to shear the material acts in


Engarc L Offset Yield Method


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf
In an FEA model, the onset of plasticity is defined by the yield stress in uniaxial direction (ie determined from supplied hardening curve) and the yield surface model you specify (for eg VonUltimate Strength Yield Point X 1000/in 2 Modulus of Elasticity (T) Tension X 1000/in 2 Compression, in terms of T Shear in terms of T in Tension (E) x 10 6 psi in Shear, in terms of E Cast iron, grey, class aStress Stress is the ratio of applied force F to a cross section areadefined as "force per unit area" tensile stress stress that tends to stretch or lengthen the material acts normal to the stressed area;



Extraordinary Tensile Strength And Ductility Of Scalable Nanoporous Graphene Science Advances



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
The external force per unit area of the material resulting in the stretch of the material is known as tensile stress What is Tensile Stress?Like the unit of tensile toughness (UT), the unit of resilience can be easily calculated by using area underneath the stress–strain (σ–ε) curve, which gives resilience value, as given below Ur = Area underneath the stress–strain (σ–ε) curve up to yield = σ × ε Ur = Pa × % = (N·m−2)· (unitless) Ur = N·m·m−3Stress σ Stress is force per unit area and can be expressed as σ = F / A (2) where σ = stress (N/m 2, lb/in 2, psi) F = applied force (N, lb) A = stress area of object (m 2, in 2) tensile stress stress that tends to stretch or lengthen the material acts normal to the stressed area
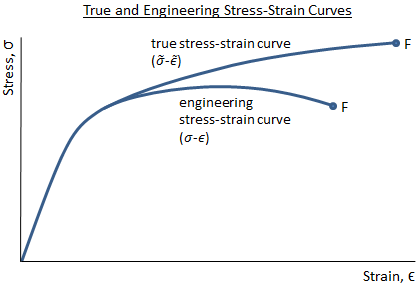


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc


Q Tbn And9gcqpjlgtnnmrjaszc Eg Tgaba Nvxolrhabne8f9t4 Gzo3vax Usqp Cau
Ultimate stress, whether it is tension, compression, shearing or bending, is the highest amount of stress a material can withstand Yield stress is the stress value at which plastic deformation occurs An accurate value for yield stress can be difficult to pinpointTensile / yield strengths and ductilities for some of the plain carbon and low alloy steels are given in the following mechanical properties of steel chart Yield Strength, Tensile Strength and Ductility Values for Steels at Room TemperatureF b = 075 F y for D / t ≤ 10, 340 / F y (SI units) is desirable that the ultimate tensile strength for the wheel should lie between the ultimate tensile strength and the yield stress of the pinion Table 32 Allowable stresses on materials for spur, helical, straight bevel, spiral bevel and hypoid bevel gears



3 1 4 A Bit More About Tensile Testing



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University
Or the amount of stress in a solid at the onset of permanent deformationSelect the unit from which you want to convert and enter the value in the respective box, the calculator will give you the converted equivalent values of other units Ultimate Strength, Breaking Strength and Yield Strength are some of the typical tensile strengthsYield point, in mechanical engineering, load at which a solid material that is being stretched begins to flow, or change shape permanently, divided by its original crosssectional area;



Plotstressstrain File Exchange Matlab Central



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com
Tensile stress is a quantity associated with stretching or tensile forces It is responsible for the elongation of the material along the axis of the applied load Tensile stress is defined asThe hardening curve specified for this model interprets yielding in the hydrostatic pressure sense the hydrostatic pressure yield stress is defined as a tabular function of the volumetric inelastic strain, and, if desired, a function of temperature and other predefined field variablesUse the following calculator to convert yield or tensile values in ksi, Mpa, N/mm² or psi Type the value in the box next to Mpa (using the drop down to change the unit of measurement) ksi MPa N/mm² psi = ksi MPa N/mm² psi


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf
.jpg)


An Introduction To The Polymer Process And Drawn Fiber
The units used for Yield Strength are N/mm^2 (Newtons per millimeter squared), which is defined as the stress the material is able to resist before it yields (elongates without being able to return elastically)The units are N/mm2 or MPa, the symbol is σbc ④ Yield Strength It refers to the stress of the metal sample during the stretching process, when the load no longer increases and the sample continues to deform The unit is N/mm2 or MPa symbol is σs The yield strength is the pressure value of the yield pointThis yield criterion can be stated in principal stress components as e = r ( I II)2 ( II III)2 ( III I)2 2 = y (52) where e is de ned as an equivalent or e ective stress and y is the yield stress measured in a uniaxial stress test This seemingly arbitrary expression can be explained by the following reasoning De ne the deviatoric stress
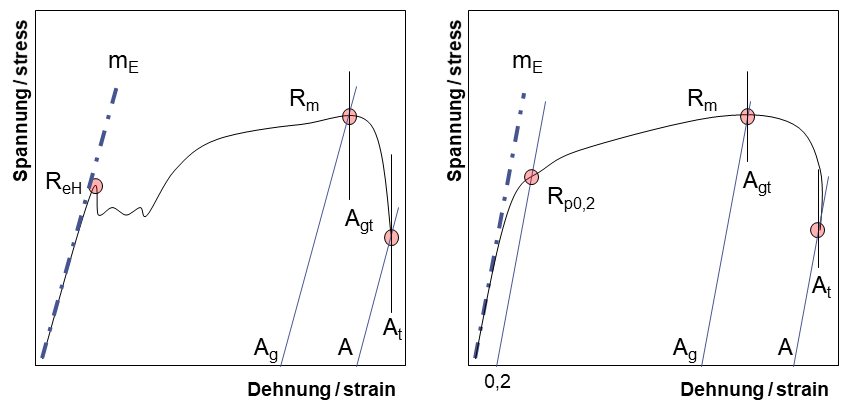


Yield Point Yield Point Ratio Offset Yield Zwickroell


How To Find Yield Strength Quora
The general formula for bending or normal stress on the section is given by Given a particular beam section, it is obvious to see that the bending stress will be maximized by the distance from the neutral axis (y) Thus, the maximum bending stress will occur either at the TOP or the BOTTOM of the beam section depending on which distance is largerAlso, the yield stress values obtained from the decreasing stress ramps are considerably lower than those obtained during the increasing stress ramps indicating again that unless sufficient time is allowed for structure rebuilding, the yield stress information obtained will be incorrect 01 1 10 100 1,000 01 1 10 100 1,000 10,000 100,000Yield stress refers to the minimum stress at which a material will deform without significant increase in load In other words, the minimum stress required to make a material flow is the yield stress, and it is a measure of the strength of the material structure


Solved The Figure Shows The Stress Strain Curve For A Mat Chegg Com



Tensile Test Experiment Materials Science And Engineering Michigan Technological University
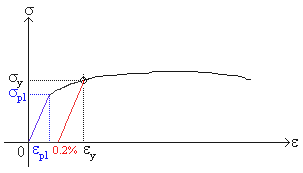
For example, aluminum has a yield strength of 14,000 pounds per square inch (or psi), copper has a yield strength of 10,000 psi, and steel, being an alloy of several different materials, has a"ratio of stress (force per unit area) along an axis to strain (ratio of deformation over initial length) along that axis" It can be used to predict the elongation or compression of an object as long as the stress is less than the yield strength of the material More about the definitions below the tableThen on the stressstrain diagram, lay off om equal to the specified value of the offset (ie yield strength ~02%), draw mn parallel to OA, and thus locate r, the intersection of mn with the stressstrain curve corresponding to load R, which is the yield strength load In recording values of yield strength obtained by this method, the value



The Strain Rate Effect Plastics Technology


Q Tbn And9gcrdlwvzddnehsqd3q4pa68yhsrtz2zujhc4jj P3hg9jteevyia Usqp Cau
The yield strength of a material represents the stress beyond which its deformation is plastic Any deformation that occurs as a result of stress higher than the yield strength is permanent Because of the linearity of elastic deformation, yield strength is also defined as the greatest stress achievable without any deviation from theThe stressstrain curve provides design engineers with a long list of important parameters needed for application design A stressstrain graph gives us many mechanical properties such as strength, toughness, elasticity, yield point, strain energy, resilience, and elongation during load It also helps in fabricationStress Measuring Yield Stress Approximate yield stress measurements can be gained by plotting the shear stress values for a range of shear rates, fitting a curve to the data, and extrapolating through the stress axis The intersect on the stress axis gives us our yield stress (figure 2)
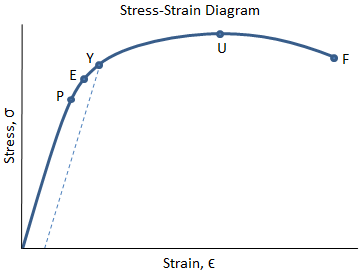


Mechanical Properties Of Materials Mechanicalc


Difference Between Stress And Strain
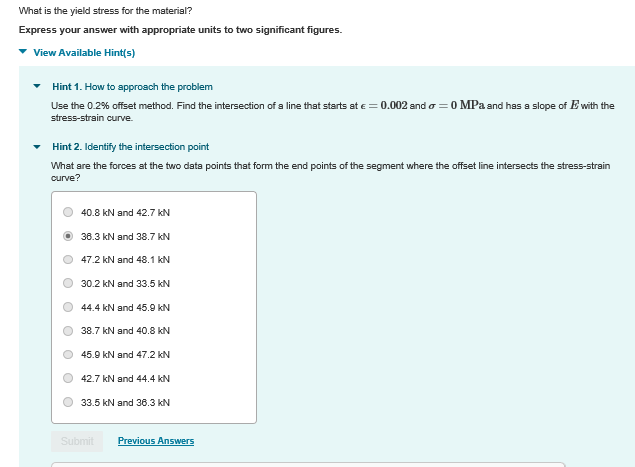


Solved What Is The Yield Stress For The Material Express Chegg Com



Ultimate Tensile Strength Wikipedia


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations


Young S Modulus Physics Forums



Yield Stress An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


The Differences Between Stiffness And Strength In Metal



What Is The Von Mises Stress And The Yield Criterion



Nondestructive Evaluation Physics Materials



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge


Mechanical Properties Nanoscience Instruments



Figure Shows The Strain Stress Curve For A Given Material What Are A Young S Modulus And B Approximate Yield Strength For This Material


Www Usna Edu Naoe Files Documents Courses En380 Course Notes Ch10 Deformation Pdf



Estimated Effects And Coefficients For Yield Stress Mean Coded Units Download Table



Modulus Of Toughness Instron


What Is The Basic Difference Between Yield Strength And Ultimate Strength For Any Elastic Material Quora


Basic Of Drillpipe Tensile Capacity And Its Calculation Drilling Formulas And Drilling Calculations



Strength At Break Tensile



What Is Tensile Testing Instron



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia


Exploring The Stress Strain Curve For Mild Steel The Chicago Curve


Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



Temperature And Strength Of Metals


Consistency Analysis Of Mechanical Properties Of Elements Produced By Fdm Additive Manufacturing Technology


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics



Bending Machines Should I Use Yield Point Or Tensile Strength Quora



Strain Ageing Of Steel Part One Total Materia Article
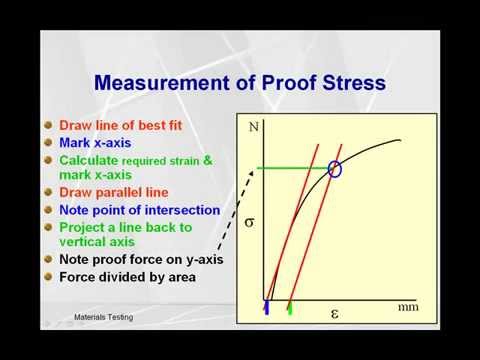


Calculate Proof Stress Youtube
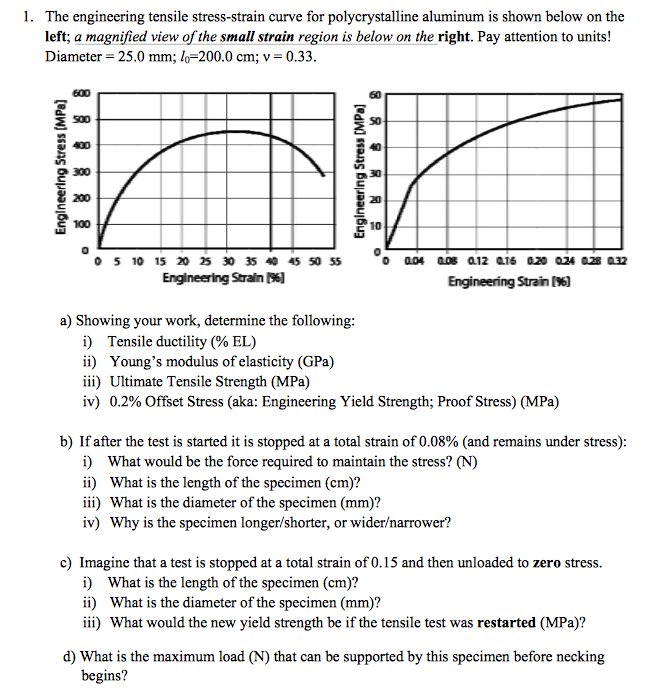


Solved The Engineering Tensile Stress Strain Curve For Po Chegg Com


Q Tbn And9gctk9iq8odyr8oad6ztec3f7a2cfwevlxhbui8zaefsdyzdh0s1n Usqp Cau



Yield Strength Strength Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge
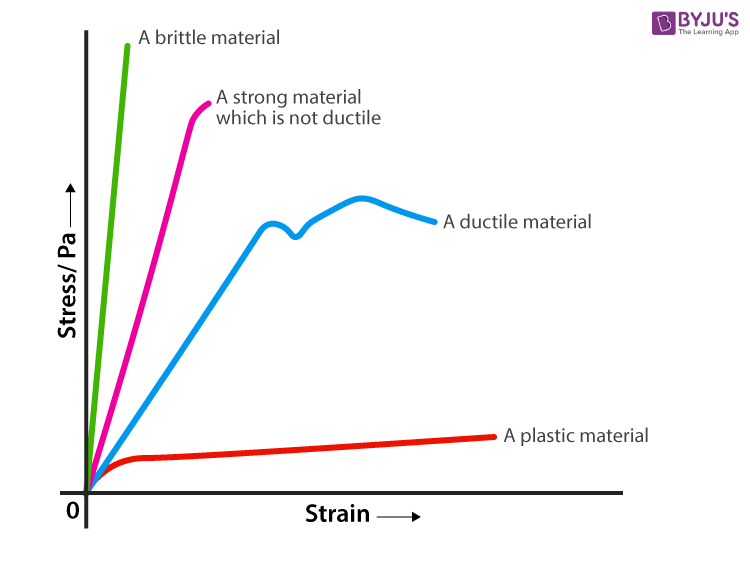


Yield Strength Definition Examples Stress Strain Graph Faqs



Shear Yield Strength An Overview Sciencedirect Topics


Http People Virginia Edu Lz2n Mse9 Chapter6c Pdf


Http Www Dept Aoe Vt Edu Aborgolt Aoe3054 Manual Expt5 D638 335 Pdf



Materials Testing Glossary Admet


Q Tbn And9gcqdhkmo7hherjjmwerev9j1zxqfwpmjetj5gvnkildcbtyau41x Usqp Cau


Http Web Mit Edu Dlizardo Www Uniaxialtestinglabreportv6 Pdf



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv



Engineering Stress Strain Curve Total Materia Article
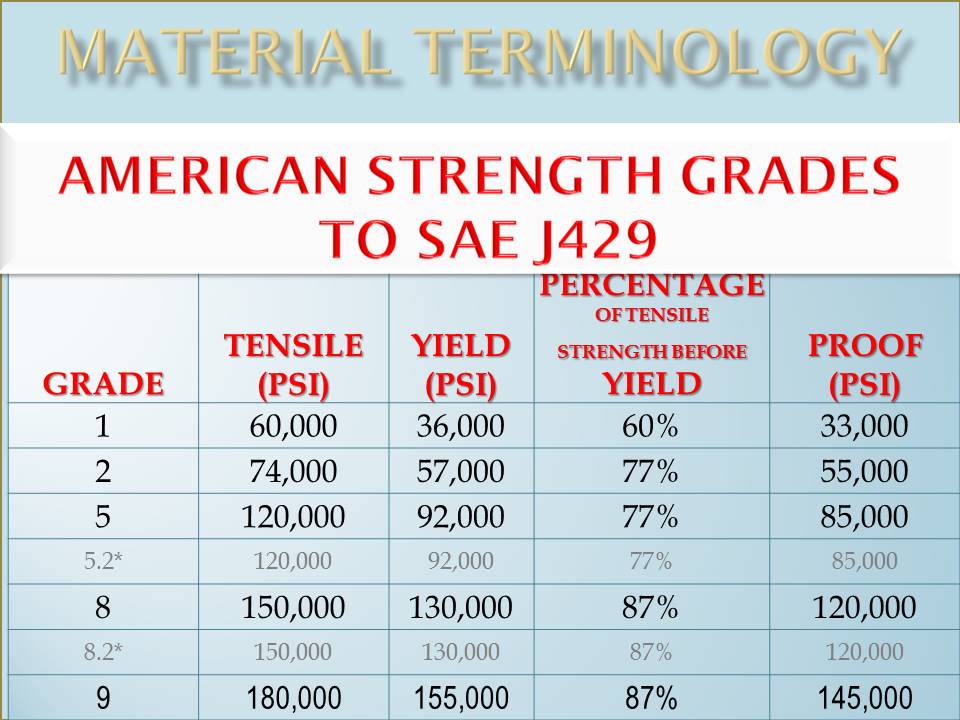


Fastenerdata Fastener Tensile Strength 10 N Fastener Specifications



Fracture Point Fracture Strength Stress Strain Curve



Stress Strain Curve Wikipedia
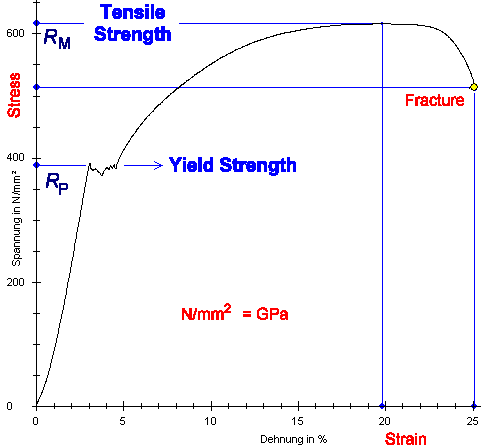


Science Of Uniaxial Deformation



Mechanics Ebook Normal Strain


Property Information



Solved Chapter 12 Problem 044 The Figure Shows The Stres Chegg Com



How To Measure Tensile Strength Elastic Modulus And Ductility Rolled Alloys Inc


Engineering Purdue Edu Xe Forms for website Fe review Slides Problemsandsolution1 Material science Problems Pdf


What Is Proof Load Of A Bolt And How Is It Different From Yield Strength Smartbolts
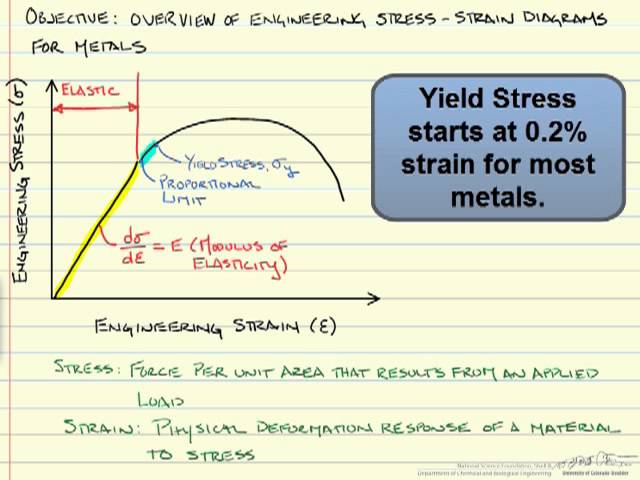


Stress Strain Diagrams Youtube
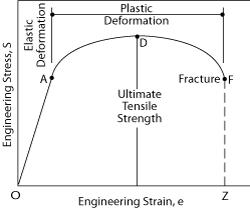


Material Properties Basic Science Orthobullets



Interspecific Variation In Beeswax As A Biological Construction Material Journal Of Experimental Biology



Materials Testing Glossary Admet


Civl 1101


What Are Tensile Strength Units Quora
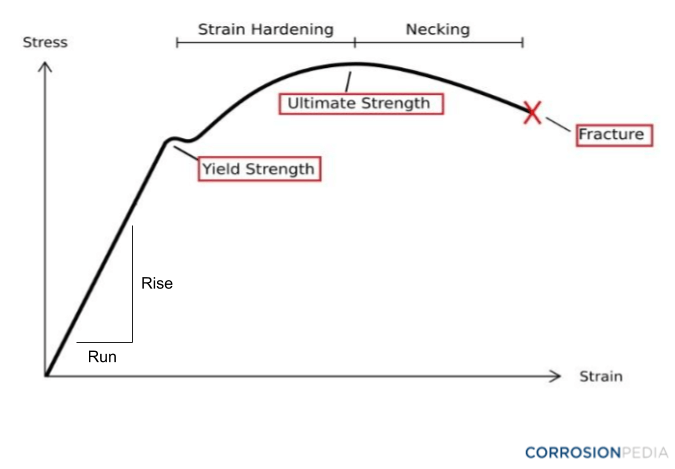


What Is A Tensile Modulus Definition From Corrosionpedia



Does Unloading Beyond Yield Point Also Affect Tensile Strength Engineering Stack Exchange



Strength At Break Tensile


Http Www Csun Edu Bavarian Courses Mse 527 Tension Test Mse 527l Pdf



Strength At Break Tensile



Mechanical Properties Of Materials Fractory
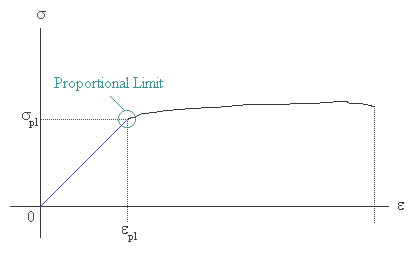


Strength And Stiffness Characteristics
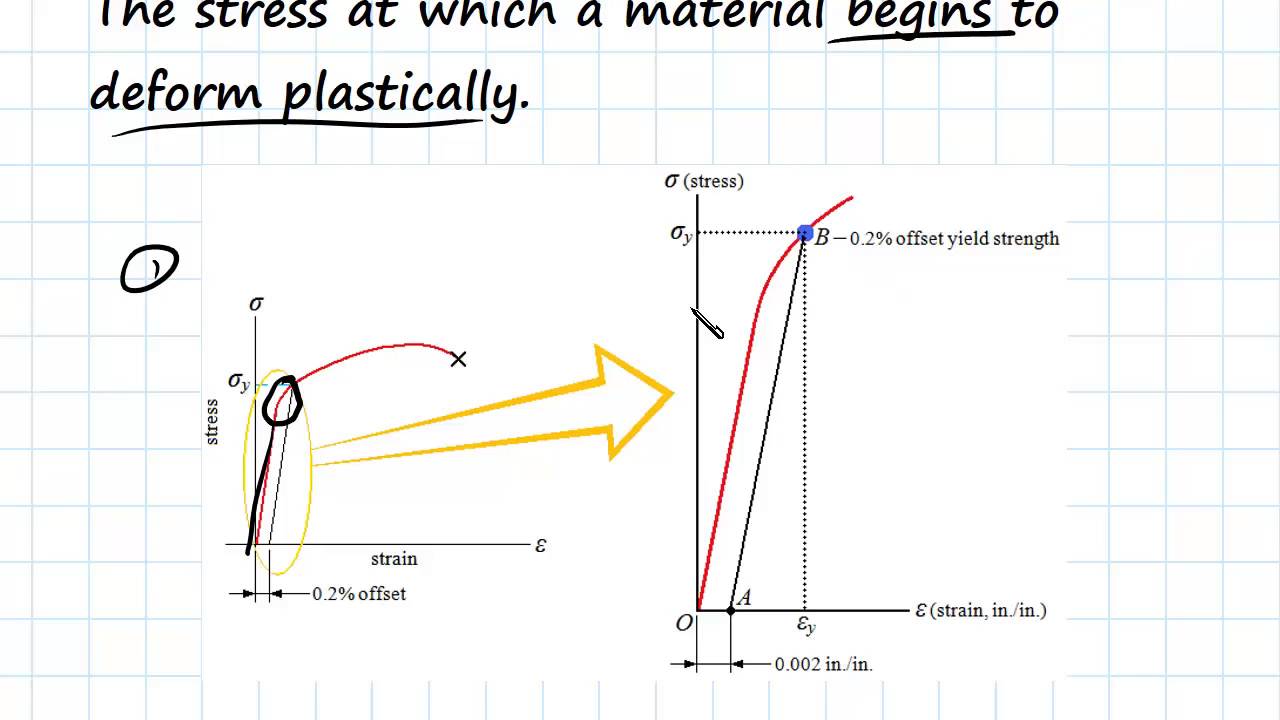


What Is The Relationship Between Yield Strength And Tensile Strength Ceramics



Poisson S Ratio N Poisson S Ratio N Units Ppt Video Online Download
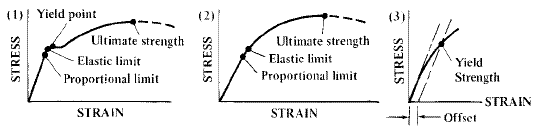


Strength Of Materials Basics And Equations Mechanics Of Materials Engineers Edge



What Is The Relation Between Tensile Strength And Young S Modulus Of A Material



What Is Yield Stress Definition Formula Video Lesson Transcript Study Com


Determining The Flow Stress Curve With Yield And Ultimate Tensile Strengths Part I
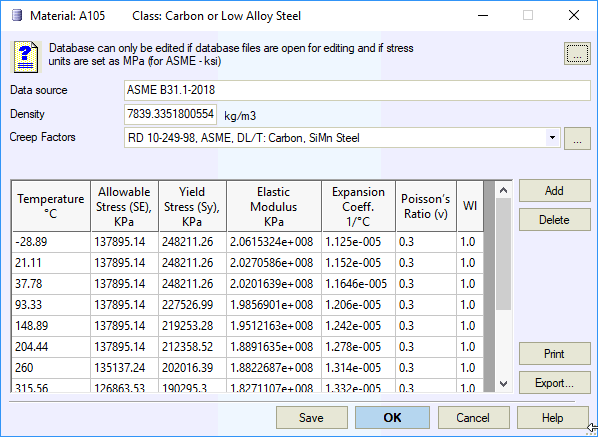


Materials Database



Engineering Fundamentals Refresh Strength Vs Stiffness Vs Hardness Fictiv
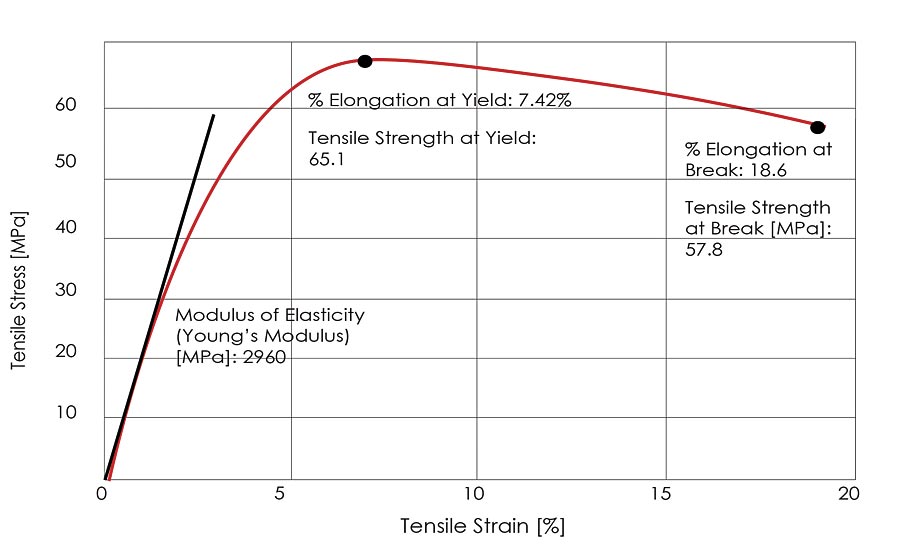


The Mechanical Properties Of Plastics 19 12 09 Quality Magazine



Tensile Strength Of Steel Vs Yield Strength Of Steel Clifton Steel



Materials Testing Glossary Admet


How Can I Determine The 0 2 Yield Stress From My Stress Strain Graphs


コメント
コメントを投稿